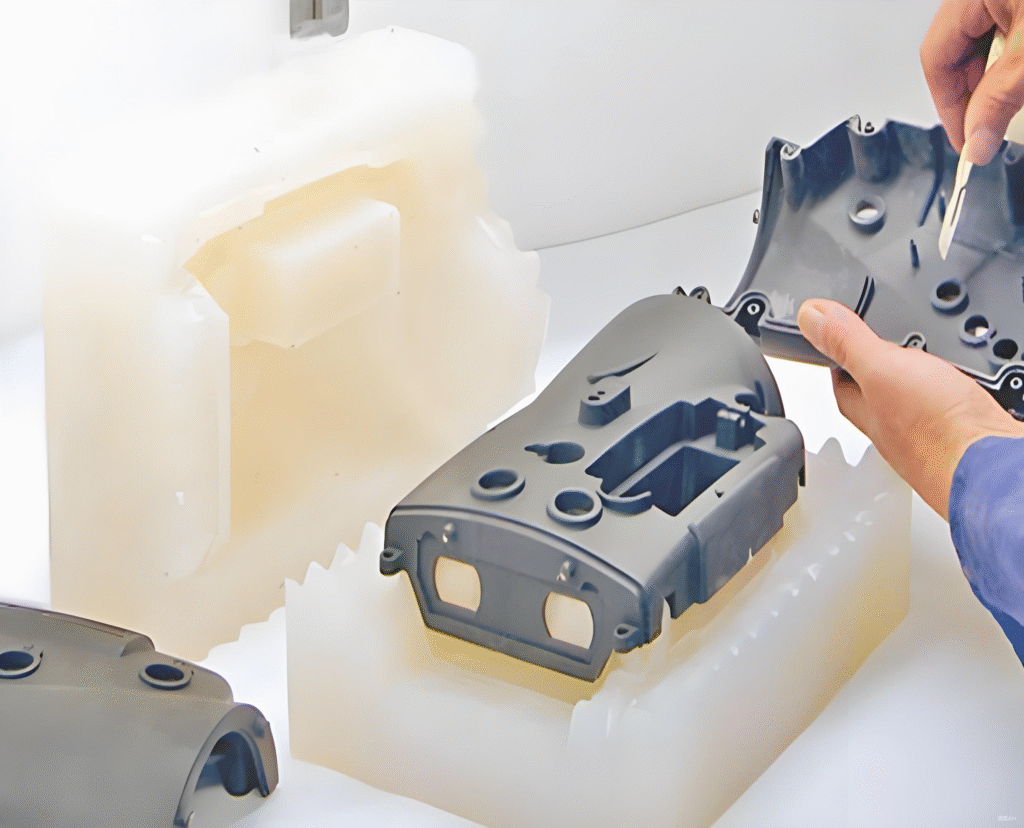
Vacuum casting is a highly versatile and efficient manufacturing process widely used across various industries for creating high-precision parts in a cost-effective manner. This technique is especially popular for rapid prototyping, small batch production, and low-volume manufacturing. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of vacuum casting, its process, materials, applications, advantages, and how it compares to other manufacturing processes.
What is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting is a method of creating prototypes and low-volume production parts by using silicone molds and a vacuum to ensure a smooth, high-quality finish on casted components. It is primarily used for replicating parts made from metals, plastics, and other materials. The process involves pouring liquid material (often polyurethane or resin) into a silicone mold under vacuum pressure to remove air bubbles and defects, allowing for precise and intricate parts to be produced.
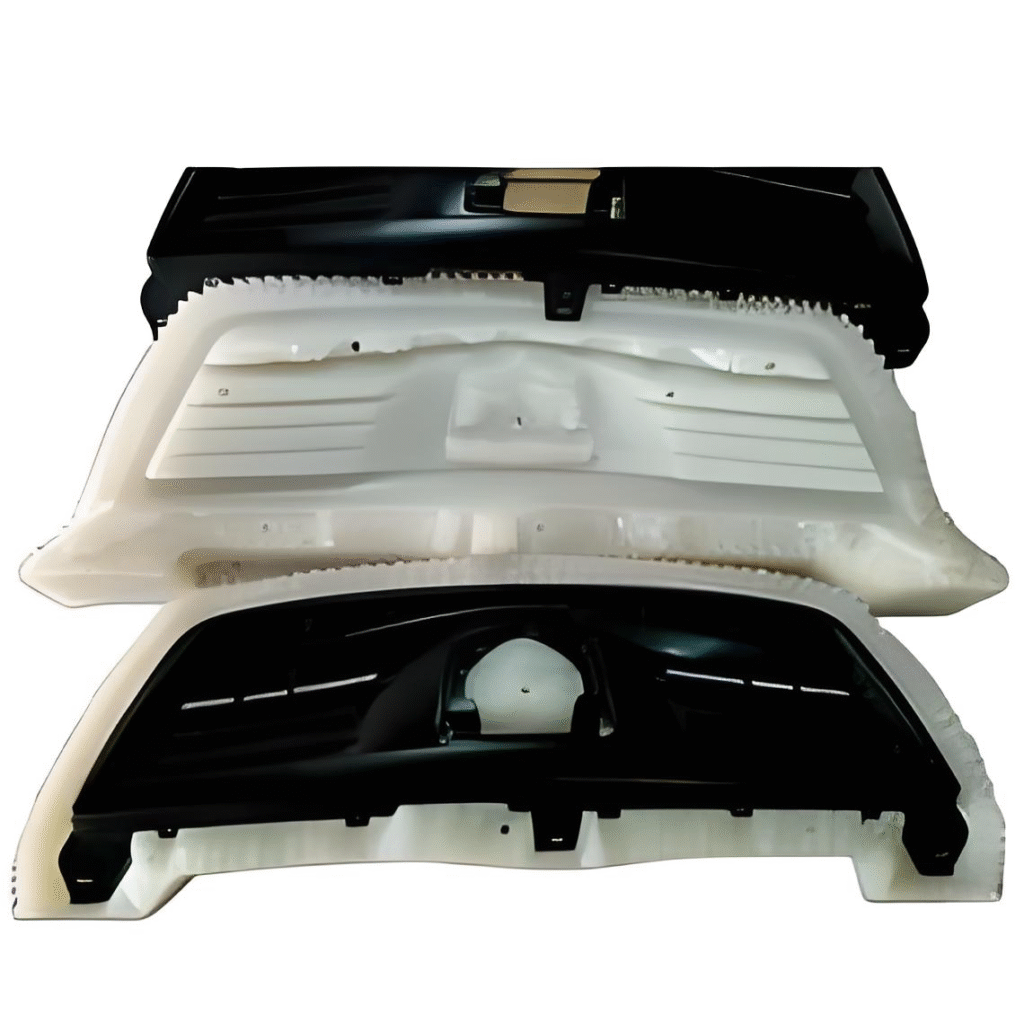
The primary appeal of vacuum casting lies in its ability to create complex geometries and high-fidelity parts in a relatively short amount of time, making it ideal for industries that require functional prototypes, small batches, or specific designs.
The Vacuum Casting Process
The vacuum casting process involves several well-defined steps to ensure high-quality results. Here’s a breakdown of the typical procedure:
Model Creation: First, prepare a master mold to make that silicone mold. It can be 3D-designed on any CAD software, like SolidWorks, CATIA, or AutoCAD. To bring the mold to life, CNC machining or 3D Printing are common choices. (Go through the next section for mold design tips.)
The accuracy of the vacuum cast parts is largely dependent on the master mold, so it needs to be as precise as possible. For that, surface polishing or grinding is an option.
Silicone Mold Making: The master model is then placed inside a container, and liquid silicone is poured around it to create a mold. The silicone mold is allowed to cure, forming a flexible, durable mold that can be used multiple times for casting.
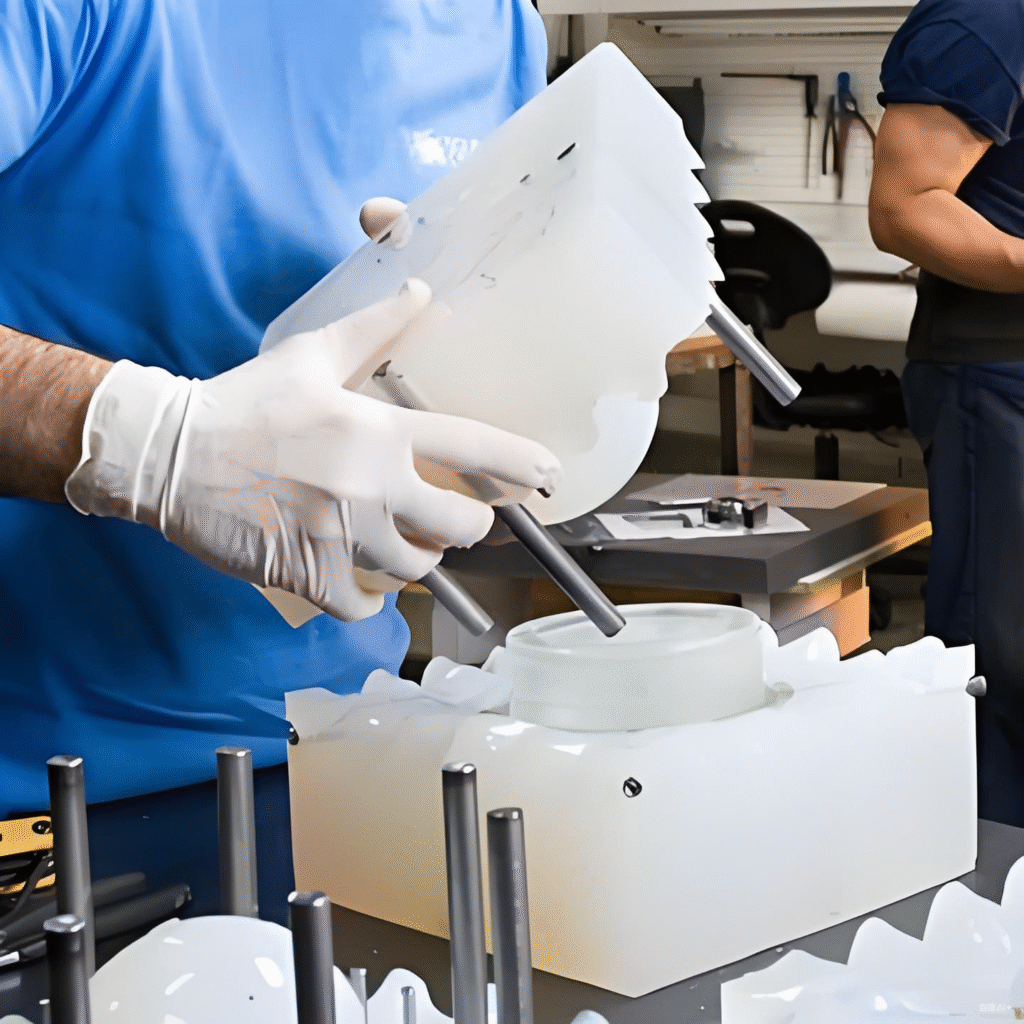

Vacuum Casting: The silicone mold is placed in a vacuum chamber where the air is removed to reduce the chance of bubbles. The casting material (usually a resin or polyurethane) is poured into the mold while under vacuum. This ensures the material fills every intricate detail of the mold.
Curing and Demolding: Once the casting material has hardened, the mold is carefully removed, revealing the final part. Depending on the material used, curing times and temperatures may vary.
Post-Processing: After demolding, the part may undergo additional post-processing steps such as trimming, painting, or surface finishing to achieve the desired appearance and functionality.
The entire process typically takes a few days, depending on the complexity and number of parts being produced, making it an efficient solution for rapid prototyping and short-run production.
Which Materials are Used in Vacuum Casting?
Several materials can be used in the vacuum casting process, each offering unique properties suited for specific applications. The most common materials include:
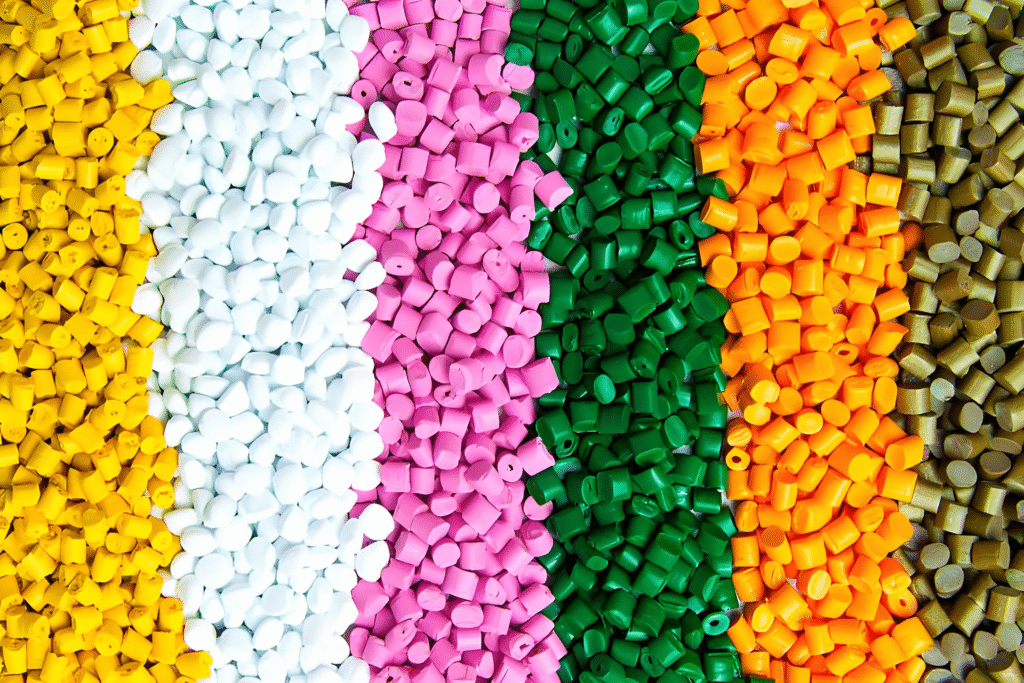

Polyurethane: Polyurethane resins are widely used for vacuum casting because of their versatility. They can be formulated to mimic a variety of other materials such as metals, plastics, and rubber, making them ideal for different industries.
Silicone: Silicone is often used for creating the mold itself because of its flexibility and ability to capture intricate details. It’s also heat-resistant, which is important for certain applications.
Epoxy Resins: Epoxies are used for parts requiring enhanced durability and resistance to wear and chemicals.
Rubber: In some cases, rubber-like resins are used to produce flexible prototypes or parts that need to absorb shock or vibration.
Metals: While less common, some metal alloys can be used for high-temperature or high-strength applications, allowing vacuum casting to create metal-like parts with excellent detail.
The choice of material depends largely on the desired properties of the finished part, such as strength, flexibility, appearance, and heat resistance.
Applications of Vacuum Casting in Various Industries
Vacuum casting is used across a wide range of industries, from automotive to aerospace, medical, and consumer electronics. Some of the key applications include:
Prototyping: The ability to create functional prototypes quickly and affordably is one of the main reasons vacuum casting is popular among designers and engineers. It allows them to test form, fit, and function without the cost and lead time associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
Automotive: Vacuum casting is used to create parts like dashboards, housings, and connectors. The process is valuable in the automotive industry, where high-quality, low-volume production is often required.
Consumer Electronics: For electronics manufacturers, vacuum casting is an excellent solution for producing prototype enclosures, buttons, and other components that require high precision and a smooth finish.
Medical Devices: In the medical field, vacuum casting is used to create parts like surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment, which require high accuracy and material integrity.
Aerospace: For the aerospace industry, vacuum casting can be used to create lightweight, durable components for aircraft interiors and systems, where precision is essential.
Fashion and Jewelry: Vacuum casting is also used to produce detailed jewelry pieces and fashion accessories, especially for prototypes and limited edition designs.
What Are the Advantages of Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting offers a range of benefits that make it an attractive option for manufacturers in various sectors. Some of the key advantages include:
Cost-Effective: Since the process does not require expensive molds or tooling like traditional injection molding, it is much more affordable, especially for small production runs.
Speed: Vacuum casting can produce high-quality prototypes or parts much faster than other traditional methods, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and quick turnaround times.
Flexibility: With the ability to use a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and rubber, vacuum casting provides flexibility in producing a wide range of parts with different properties.
Complex Geometries: The vacuum casting process allows for the creation of highly detailed and complex shapes that may be difficult or expensive to achieve using other methods.
Low-Volume Production: Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that are better suited for mass production, vacuum casting excels in creating low-volume runs without sacrificing quality or increasing costs.
Comparison of Vacuum Casting with Other Processes: 3D Printing, Injection Molding
When comparing vacuum casting to other manufacturing processes like 3D printing and injection molding, each method has its strengths and weaknesses.
1. Vacuum Casting vs. 3D Printing
Speed: Vacuum casting tends to be faster than 3D printing, especially when creating multiple parts at once.
Surface Finish: Vacuum casting provides a smoother surface finish compared to 3D printed parts, which often require additional post-processing.
Material Options: While 3D printing offers a variety of materials, vacuum casting typically provides a broader range of properties, including the ability to mimic metal and rubber finishes.
2. Vacuum Casting vs. Injection Molding
Cost: Injection molding is cost-effective for mass production but requires expensive molds and tooling. In contrast, vacuum casting is more affordable for small batches and prototypes.
Lead Time: Injection molding has longer lead times due to mold creation, whereas vacuum casting can produce parts much more quickly.
Flexibility: Vacuum casting is more flexible for rapid changes in design and material, whereas injection molding requires significant retooling for design changes.
Conclusion
Vacuum casting is a powerful and cost-effective manufacturing process that offers a wide range of benefits, from rapid prototyping to low-volume production. Its versatility in material selection, ability to produce complex geometries, and fast turnaround times make it an ideal choice for industries ranging from automotive to medical devices and consumer electronics. Compared to other processes like 3D printing and injection molding, vacuum casting stands out for its combination of precision and affordability in small-batch production.
At Precionn, we specialize in precision machining and vacuum casting services, ensuring high-quality and reliable parts for your business needs. Whether you require rapid prototyping or low-volume production, we are here to help you achieve your goals with speed and accuracy. For more information about our vacuum casting services, contact us today!