Kovar machining services
Kovar alloy (typical grade such as 4J29) is an iron-nickel-cobalt glass-sealing alloy that is widely used in electrovacuum, optical communication and semiconductor packaging fields because its coefficient of thermal expansion matches that of borosilicate glass.
-
15+ years of Kovar machining experience
-
Competitive prices
- Fast delivery


What is Kovar?
Kovar alloy is an iron-nickel-cobalt based, low-expansion alloy with a coefficient of thermal expansion highly compatible with inorganic materials such as borosilicate glass and alumina ceramics. Within the temperature range of -60℃ to +400℃, its coefficient of thermal expansion (approximately 4.7 × 10⁻⁶/℃) is almost identical to that of borosilicate glass (such as Pyrex glass). When the temperature changes, the alloy and glass expand and contract with the same degree, preventing stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction, thus avoiding encapsulation cracking and leakage. Kovar alloy has excellent machinability and can be forged, rolled, stamped, welded, and other conventional processes to produce various shapes of device components such as leads, housings, and supports.
Precionn provides Kovar alloy CNC machining to producing high-quality metal parts with tight tolerances and complex geometries. Here’s what you need to know about kovar alloys and their CNC machining.
Kovar alloy Properties
Kovar alloy Physical properties
- Kovar alloy density:8.3 g/cm³
- Kovar alloy thermal expansion properties :4.7×10⁻⁶/℃(-60℃~+400℃ )
- Kovar alloy Tensile strength :The annealed state has a strength of approximately 550 MPa, while the cold-worked state can reach over 800 MPa.
- Kovar alloy hardness:The hardness is approximately 160 HB in the annealed state, and it will increase significantly after cold working.
- Kovar alloy Melting point :1450℃
- Kovar alloys have weak magnetic properties
Kovar alloy Chemical composition
| chemical composition | percentage(%) | The role of chemical components |
| Fe | 52~56 | Matrix elements ensure the basic mechanical properties of the alloy. |
| Ni | 28~30 | Lowering the coefficient of thermal expansion of the alloy improves its compatibility with glass. |
| Co | 16~18 | Synergistic nickel adjustment modulates the coefficient of thermal expansion, while simultaneously improving the alloy’s machinability and weldability. |
| Mn | ≤0.5 | Deoxidation and desulfurization optimize the casting and rolling properties of the alloy. |
| Si | ≤0.3 | Deoxidizers enhance the oxidation resistance of alloys. |
| C | ≤0.05 | Controlling the hardness and toughness of the alloy is crucial; excessive amounts can reduce sealing reliability. |
| P | ≤0.02 | Harmful impurities must be strictly controlled to avoid the formation of brittle phases. |
Application industries of Kovar alloy
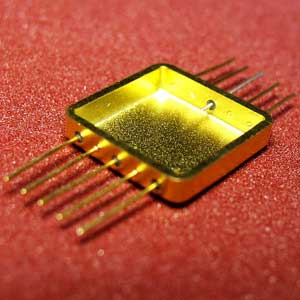
Semiconductor packaging
In ceramic packaging, it serves as a cap, lead frame, or package base, mating and sealing with the ceramic substrate to protect the chip from external environmental influences.

electron vacuum tube
Kovar is used to manufacture housings and leads for devices such as microwave tubes, traveling wave tubes, magnetrons, lasers, and X-ray tubes, achieving hermetic seals between glass or ceramics and metals to ensure high internal vacuum.

Aerospace
Kovar is used to manufacture sealing housings and connectors for high-reliability avionics, missile guidance systems, and satellite communication equipment.

Photovoltaics and solar energy
Kovar is used in the manufacture of CPV and space solar cells as a transition sheet between the cell and the heat sink, effectively buffering thermal stress caused by temperature changes and preventing the brittle cells from cracking.
Optoelectronics and optical communication
Kovar is used to package high-power laser diodes, LEDs, and coupling devices for fiber optic communications, achieving reliable sealing between optical components and metal housings, ensuring clean and long-term stable optical paths.
Medical devices
Kovar is used for sealed housings in implantable medical devices (such as pacemakers and neurostimulators) and detector assemblies in some high-end medical devices (such as CT and MRI machines). machines). optical paths.
Kovar machining FAQs
Kovar alloy is a low-expansion iron-nickel-cobalt alloy that is highly compatible with inorganic materials such as glass and ceramics, and is often used for sealing connections between glass or ceramics and metals.
Kovar alloys are mainly used in industries such as semiconductor packaging, electronic vacuum devices, aerospace, and medical equipment.
After processing with Kovar, an annealing process is added, holding the material at 600-650℃ for 1-2 hours and then slowly cooling it in the furnace. This can significantly improve the material's dimensional stability and ductility.
Machining Kovar alloys requires specialized cutting tools, such as PCD alloy and ceramic tools, to improve tool wear resistance, overcome hardening during machining, and increase machining efficiency.
Welding is a critical process in the processing of Kovar alloys. Commonly used welding methods include brazing, TIG welding, and resistance welding.
