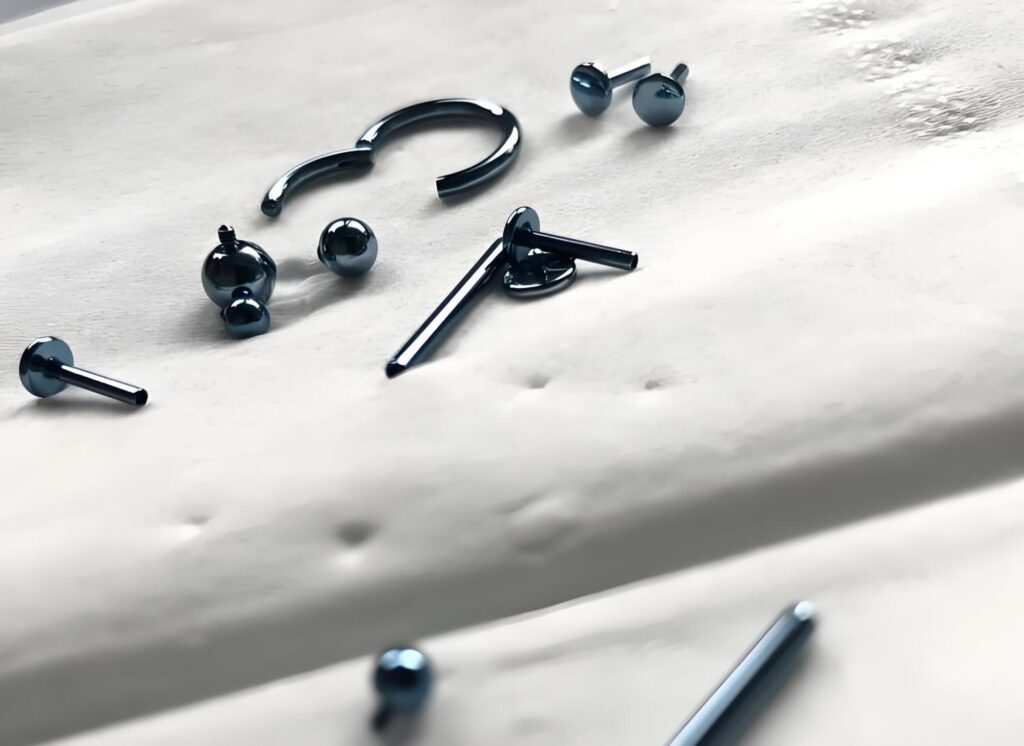
Anodized titanium has gained remarkable popularity in recent years, appreciated for its striking appearance, enhanced durability, and excellent resistance to corrosion. From aerospace components to jewelry design, titanium anodizing combines functionality with aesthetics, offering a finish that’s both high-performance and visually distinctive.
Understanding the titanium anodization process, along with its benefits and limitations, is essential for engineers, manufacturers, and designers seeking reliable and long-lasting metal finishes.
What Is Anodized Titanium?
Anodized titanium refers to titanium that has been treated through an electrochemical anodizing process. Unlike traditional coatings or paint applications, anodizing doesn’t deposit any external material onto the surface. Instead, it alters the natural oxide layer of titanium, increasing its thickness and producing a variety of brilliant anodized titanium colors—all without using dyes or pigments.

This color effect results from light interference within the oxide layer. By carefully controlling the voltage applied during anodization, different shades emerge—from gold and blue to vivid purples and greens.
Because the color originates from the metal’s surface structure, titanium anodization is environmentally friendly, long-lasting, and resistant to fading or peeling.
Why Anodize Titanium?
Titanium is naturally corrosion-resistant, but anodizing enhances its properties even further. Below are the key advantages:
1. Superior Corrosion Resistance
The anodized oxide layer acts as a robust barrier, protecting titanium from moisture, chemicals, and salt exposure—especially useful in marine, medical, and aerospace environments.
2. Aesthetic Versatility
Anodized titanium colors provide designers and manufacturers with endless creative options. Since the hues depend on voltage, not pigments, each piece can achieve a unique metallic finish.
3. Enhanced Surface Hardness
The anodizing process increases surface hardness, improving scratch resistance and wear performance—important for tools, implants, and precision components.
4. Biocompatibility
Titanium anodize finishes are completely biocompatible, making them ideal for medical implants, dental devices, and surgical instruments that come into contact with human tissue.
5. Environmentally Friendly Process
Because anodization relies on electricity rather than harsh chemicals or paints, it’s a sustainable finishing method aligned with modern green manufacturing standards.
The Titanium Anodizing Process
The titanium anodization process involves several carefully controlled stages to achieve consistent results. Whether performed with an industrial titanium anodizing system or a small titanium anodizing kit, the steps remain similar:
- Surface Preparation
The titanium surface is thoroughly cleaned and polished to remove dirt, grease, and oxide contaminants. This ensures even color development. - Electrolyte Bath
The prepared part is immersed in an electrolyte solution, typically containing phosphoric or sulfuric acid. - Applying Voltage
A specific electrical voltage is applied to the titanium piece. The voltage determines the thickness of the oxide layer, which in turn defines the resulting anodized titanium color. - Rinsing and Drying
After anodization, parts are rinsed in deionized water and dried, revealing a bright, durable, and colorful finish.
Industrial facilities use precision-controlled power supplies and electrolyte conditions to ensure repeatability and uniformity, especially for aerospace or medical applications.
Applications of Anodized Titanium
The versatility of titanium anodizing makes it an ideal choice across a wide range of industries:
Medical and Dental Applications
The biocompatibility of anodized titanium makes it perfect for implants, orthopedic screws, and surgical instruments, where safety and corrosion resistance are essential.
Aerospace and Automotive Engineering
Lightweight anodized titanium parts resist heat, oxidation, and mechanical stress, making them valuable for jet engines, exhaust systems, and performance vehicles.
Jewelry and Fashion
Anodized titanium jewelry is admired for its vibrant colors, lightweight feel, and hypoallergenic properties—common in rings, earrings, and watch components.
Sports and Outdoor Equipment
From bicycle parts to climbing gear, anodized titanium combines strength and low weight, offering both beauty and endurance.
Architecture and Interior Design
Designers use anodized titanium panels and fixtures to create futuristic, color-rich accents that remain maintenance-free for years.
Challenges and Limitations of Anodized Titanium
Despite its advantages, titanium anodization does have certain limitations that professionals should consider:
- Surface Scratches: While harder than untreated titanium, the anodized surface can still scratch under high friction.
- Color Variability: Achieving consistent anodized titanium colors requires expert voltage control and clean surface conditions.
- Moderate Chemical Resistance: Although corrosion-resistant, anodized titanium may degrade in highly acidic or alkaline environments.
- DIY Limitations: Home anodizing kits can yield uneven colors compared to professional anodizing systems used by industrial service providers.
Understanding these limitations helps determine when anodized titanium is the most suitable solution.
Precionn: Your Partner for Titanium Anodizing Services
At Precionn, we combine technical precision with a deep understanding of material science to deliver reliable titanium anodizing services for global industries. From custom aerospace parts to decorative titanium components, our team ensures every anodized surface meets the highest standards of quality, color accuracy, and durability.
Our expertise covers every stage—from machining titanium parts to surface finishing—helping clients achieve visually stunning and functionally robust results.
Conclusion
Anodized titanium exemplifies the perfect fusion of beauty, strength, and performance. Its unique electrochemical treatment enhances corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and visual appeal without the need for paints or coatings. Whether used in high-tech aerospace assemblies or elegant jewelry designs, titanium anodization remains one of the most advanced and eco-friendly finishing methods available today.
At Precionn, we are dedicated to precision engineering and advanced finishing solutions that help clients across industries realize the full potential of titanium. If you’re looking for a trusted partner for titanium anodizing services, our experts can guide you toward optimal results—combining science, craftsmanship, and sustainability.
FAQ: Common Questions About Anodized Titanium
Over time, anodized titanium colors may appear less vibrant due to wear or surface abrasion. However, fading does not mean the oxide layer has disappeared.
The oxide layer formed through anodization is integral to the metal. It does not peel or chip away like paint but can wear down with heavy use.
In industrial settings, the process is relatively quick, often taking only a few minutes once the setup is complete.
Titanium does not rust in the conventional sense, and anodization further enhances its resistance to oxidation and corrosion.




