When it comes to strong, affordable materials for manufacturing and machining, galvanized steel remains one of the most trusted options. At Precionn, a leader in precision machining, we’ve seen how this material offers an ideal balance of performance, corrosion resistance, and longevity.
But a question often arises: Does galvanized steel rust?
The short answer—not easily, but it can under certain conditions.
This guide explores how galvanized steel resists corrosion, what can cause it to rust, and how to protect and maintain it for long-term use.
What Is Galvanized Steel and Why Doesn’t It Rust Easily?
Galvanized steel is regular steel coated with a layer of zinc, which serves as a protective barrier against rust and corrosion. This zinc layer prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the steel underneath.
Unlike paint or sealants, zinc provides sacrificial protection—it corrodes first, shielding the steel beneath it. That’s why even if the surface is scratched, the zinc continues to protect exposed areas nearby.
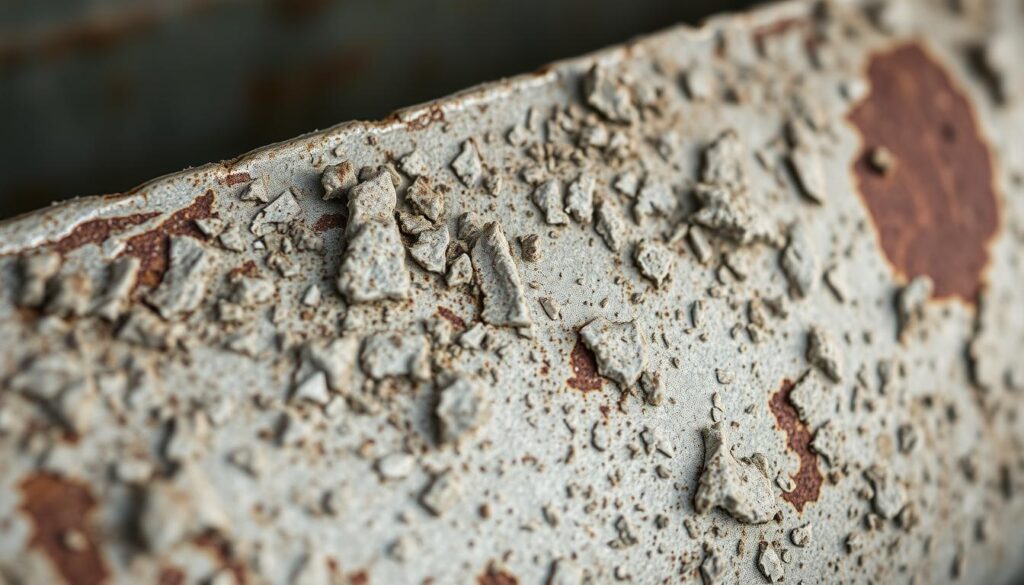
However, while galvanized steel is extremely rust-resistant, it’s not completely rust-proof. Once the zinc coating wears away or is damaged, the exposed steel can begin to corrode.
How Long Does Galvanized Steel Last?
The lifespan of galvanized steel depends on several factors:
- Zinc Coating Thickness: Thicker coatings—such as those from hot-dip galvanizing—offer stronger, longer-lasting protection than electro-galvanized coatings.
- Environment: Coastal or industrial environments with salt or pollutants can accelerate zinc corrosion.
- Maintenance and Handling: Proper storage, cleaning, and periodic inspections significantly extend the material’s life.
In most outdoor environments, galvanized steel can last 20 to 50 years, and sometimes even longer under mild conditions. In rural areas with clean air and low humidity, it may remain rust-free for decades.
Common Causes of Rust on Galvanized Steel
Even with its corrosion-resistant coating, galvanized steel can rust if exposed to extreme or prolonged stress. Here are the most common causes:
1. Harsh or Polluted Environments
High humidity, salty air (especially near coastlines), and industrial pollution can break down the zinc coating. Over time, this may lead to white rust (zinc oxide), which, while not as harmful as red rust, still indicates surface degradation.
2. Physical Damage
Scratches, dents, or abrasions during machining or installation can expose bare steel, allowing moisture and oxygen to initiate corrosion. Proper handling and tooling help prevent such damage.
3. Continuous Moisture Exposure
Standing water or poor drainage can accelerate zinc corrosion. Applications like outdoor furniture, fences, or roofing are especially at risk if water pools on the surface.
4. Chemical Reactions
Certain acids and chemicals—including industrial cleaners and runoffs—can degrade zinc. Avoid contact with copper, untreated wood, or other reactive materials that may cause galvanic corrosion.
How to Prevent Rust on Galvanized Steel
With the right care, you can keep galvanized steel looking and performing like new for decades. Here are some proven strategies:
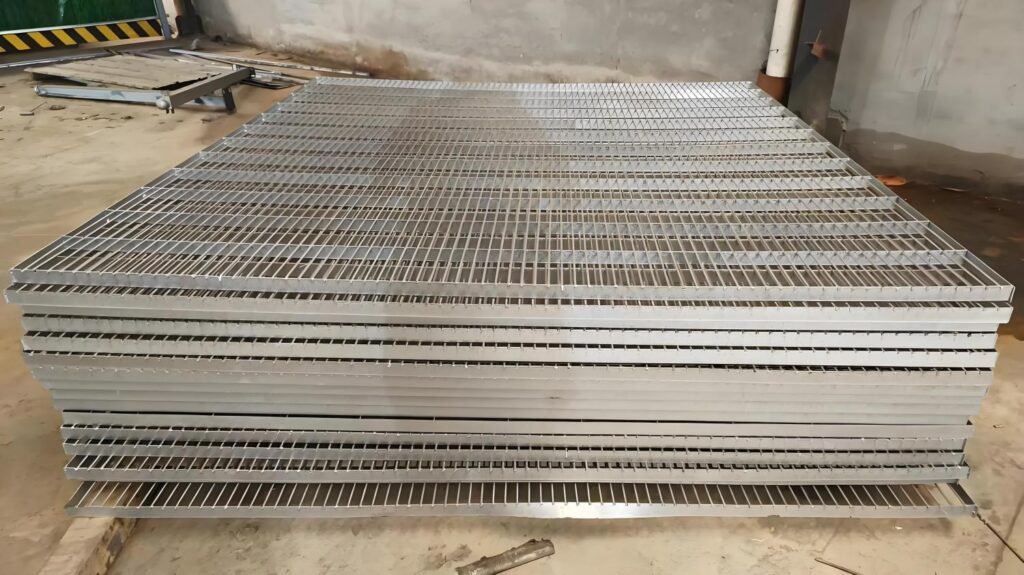

Select the Right Type of Galvanizing
Choose hot-dip galvanized steel for heavy-duty applications exposed to weather, as it provides a thicker, more durable coating than electro-galvanized steel.
Inspect Regularly
Check surfaces for scratches, white rust, or dull spots. Early detection allows for small touch-ups before corrosion spreads.
Apply Protective Coatings
Use zinc-rich primers, sealants, or compatible paints to reinforce protection—especially after cutting or welding. These coatings help restore any compromised areas.
Store and Handle Properly
Keep galvanized steel in a dry, ventilated area. Avoid stacking materials where water can get trapped between sheets or components.
Manage Environmental Exposure
Reduce direct exposure to moisture and pollutants by improving drainage, using covers, or installing protective barriers in coastal zones.
What If Galvanized Steel Starts to Rust?
If rust does appear, it usually means the zinc coating has worn away in spots. Fortunately, cleaning and restoring galvanized steel is straightforward.
Step-by-Step Restoration
- Assess the Rust: Determine if corrosion is surface-level or structural.
- Clean Gently: Wash with mild soap and water using a soft brush—avoid harsh abrasives.
- Remove Rust: For light rust, use fine sandpaper or a nylon brush. For tougher spots, a 1:1 vinegar and water mix can help dissolve corrosion.
- Apply Zinc-Rich Paint: After drying, cover the area with cold galvanizing spray or zinc-rich primer to rebuild the protective barrier.
- Seal and Protect: Optionally, add a clear protective coating to prevent moisture intrusion.
If rust is extensive or structural integrity is compromised, professional assessment and replacement may be necessary.
Working with Galvanized Steel in Machining
Galvanized steel is widely used in precision machining due to its strength and versatility—but it requires proper technique:
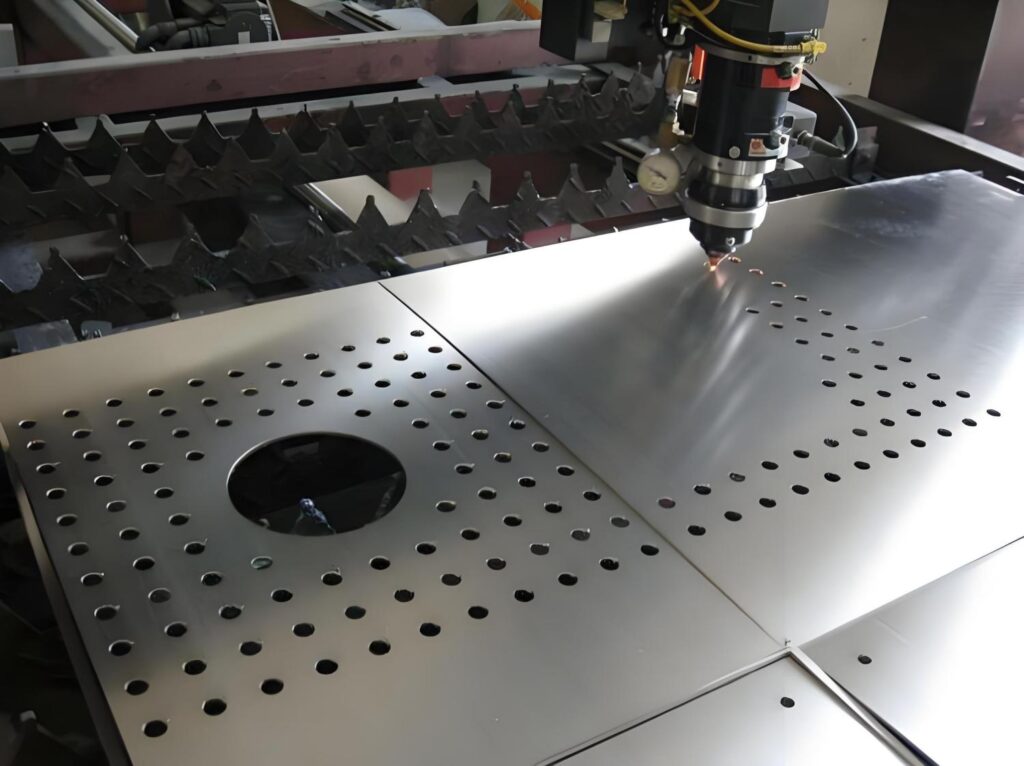
- Cutting and Welding: The zinc layer can produce fumes when heated; ensure good ventilation and use tools designed for galvanized materials.
- Edge Protection: After machining, reapply zinc-based coatings to any exposed steel edges.
- Material Compatibility: Avoid pairing galvanized steel with dissimilar metals like copper or aluminum in moist environments to prevent galvanic corrosion.
At Precionn, our machining experts apply industry best practices to maintain coating integrity and deliver high-quality, rust-resistant components.
Why Choose Galvanized Steel for Your Projects
From construction and automotive manufacturing to precision engineering, galvanized steel remains a smart investment. It offers:
- Long-term corrosion resistance
- High strength-to-cost efficiency
- Low maintenance requirements
- Compatibility with machining and fabrication processes
By understanding how galvanized steel behaves and maintaining it properly, you can ensure decades of reliable performance in even the toughest environments.
At Precionn, we combine advanced machining techniques with material expertise to help clients worldwide achieve durable, high-precision results. Whether you need advice on material selection or custom machining for galvanized components, our specialists are here to support your goals.




