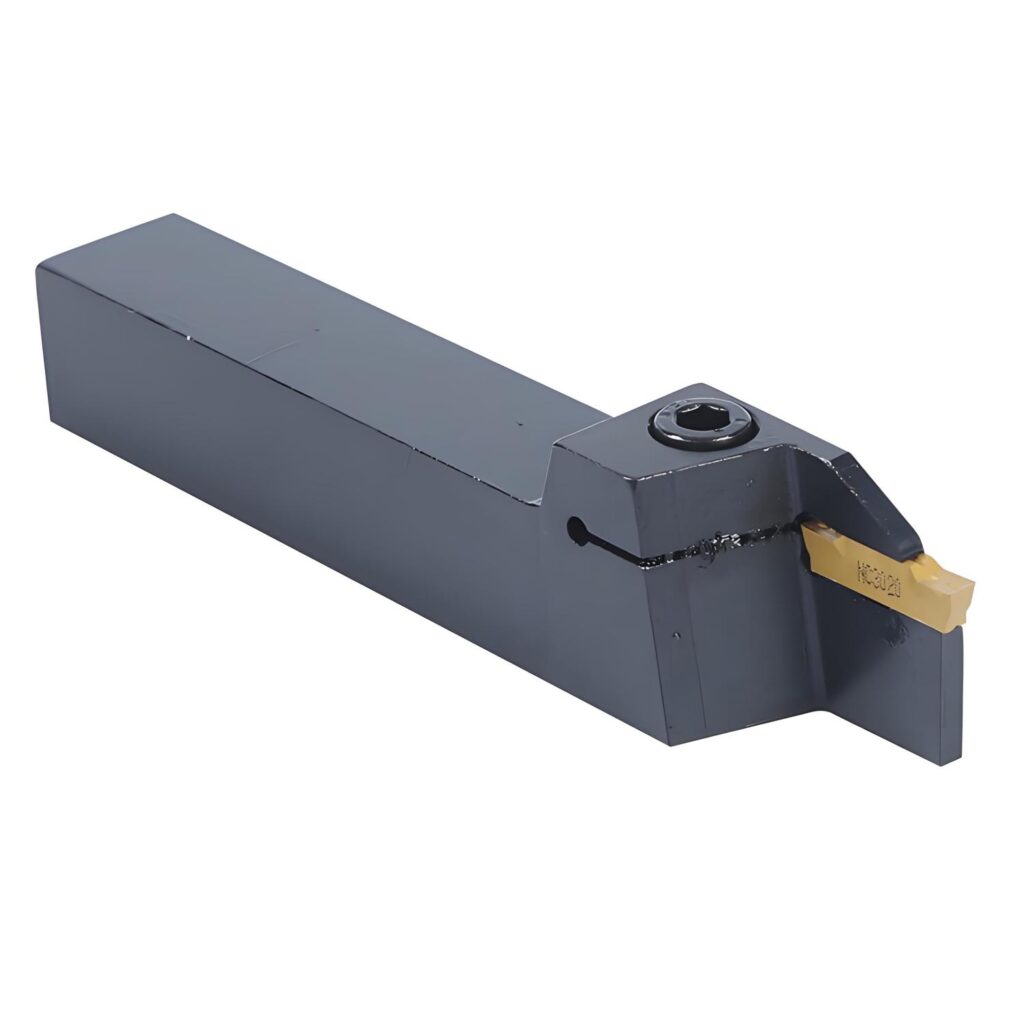
In the machining world, cutting tools play a crucial role in ensuring precise, clean, and efficient operations. Among these, the lathe parting tool stands out as a must-have for separating finished components from raw stock and creating accurate grooves. Though it might seem like a simple accessory, the right parting tool can make a significant difference in production quality, efficiency, and safety.
This guide will cover the essential aspects of lathe parting tools, including their types, materials, key performance factors, maintenance, and practical tips for selecting the right tool for each project.
What is a Lathe Parting Tool?
A lathe parting tool is designed specifically for turning operations where the goal is to cut through a workpiece cleanly, separating it from the remaining material. Unlike shaping or finishing tools, parting tools focus on precision cuts rather than forming or contouring.
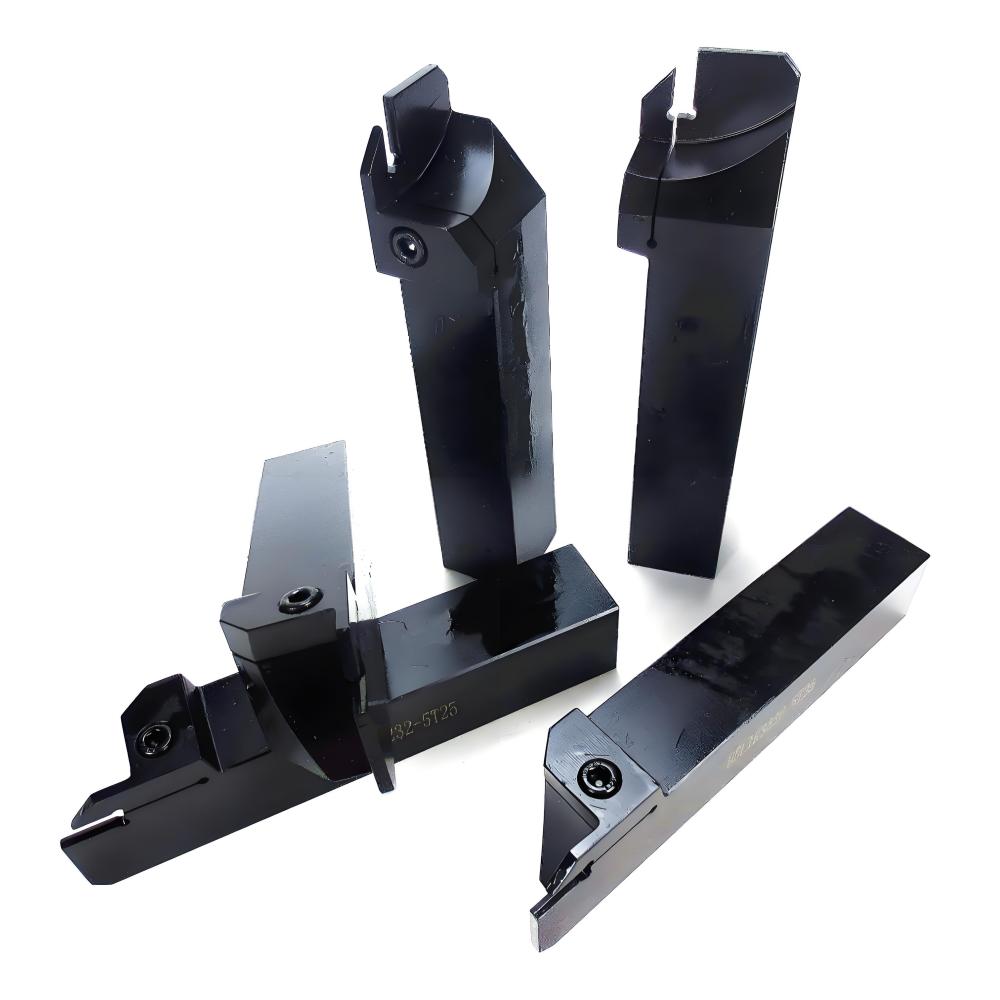

Applications in Machining
- Cutting finished parts from bar stock.
- Making grooves, recesses, or slots.
- Preparing workpieces for threading, polishing, or assembly.
- Ensuring precise separation in high-speed turning operations.
Parting tools are widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and general metal fabrication, where precision and clean cuts are crucial.
Common Types of Lathe Parting Tools
Different types of lathe parting tools are available to meet a variety of machining needs. Choosing the right type enhances cutting efficiency and improves the final surface finish.
Single-Point Parting Tools
These tools feature a narrow cutting edge designed for straight, accurate cuts. They are particularly effective for metals like steel, aluminum, and brass. Single-point parting tools offer excellent control and are a reliable choice for standard machining tasks.
Tapered Parting Tools
Tapered tools reduce friction along the cut, improving chip flow and extending tool life. They are ideal for high-speed or high-volume production where consistent performance is required.
Notched Parting Tools
The notched design allows for groove cutting while reducing cutting resistance. Notched tools are often used to minimize stress on the lathe and workpiece during separation.
Carbide-Tipped Parting Tools
Carbide-tipped parting tools are extremely durable and maintain their sharp edge under heavy-duty conditions. They are suitable for hard metals and demanding applications, where standard steel tools may fail.
Material and Selection of Lathe Parting Tools
Choosing the right material is essential to get the best performance from a lathe parting tool.
Common Tool Materials
- High-Speed Steel (HSS) HSS is versatile, providing a good balance of toughness and wear resistance. It is easy to sharpen and works well for low-to-medium volume operations.
- Carbide Carbide is extremely hard and wear-resistant, maintaining its edge longer than HSS. It is ideal for high-speed machining and cutting hard metals, although it is more brittle and requires careful handling.
- Cermet and Ceramic These materials are used in high-temperature and ultra-precision applications. Cermet combines ceramic and metal properties for exceptional hardness, thermal resistance, and durability.
How to Select the Right Tool Material
- Match the tool to the workpiece material: soft metals like aluminum suit HSS, while hardened steels often require carbide.
- Consider production volume: higher-volume jobs benefit from more durable materials like carbide.
- Factor in cutting conditions, including speed, depth, and lubrication, to choose a material that maintains performance and reduces wear.
Factors Influencing Lathe Parting Tool Performance
Several variables impact the effectiveness of parting tools:
Cutting Speed
The speed of the cut affects both finish quality and tool longevity. Too fast may overheat the tool, while too slow can cause poor chip removal.
Feed Rate and Depth of Cut
Balanced feed and cut depth are key. Aggressive cuts can damage the tool, while conservative cuts may slow production. Optimal settings depend on the material and tool type.
Tool Geometry
The cutting edge shape and angles influence efficiency and chip flow. Sharper edges deliver clean cuts but wear faster, while slightly rounded edges improve durability at the expense of minor surface finish quality.
Lubrication and Cooling
Proper lubrication reduces friction and heat, protecting both the tool and workpiece. Coolants are especially important when machining hard metals or operating at high speed.
Lathe Parting Tool Maintenance and Usage Tips
Maintaining parting tools ensures consistent results and extends tool life.
Inspection
Regularly check for wear, chipping, or dull edges. Worn tools can affect cut quality and put strain on the lathe.
Sharpening
Maintain the original cutting geometry when sharpening. Over-sharpening reduces strength, while under-sharpening limits cutting efficiency.
Storage and Handling
Store tools in a clean, dry place. Handle carbide and ceramic tools carefully as they are brittle and prone to chipping.
Best Usage Practices
- Align the tool with the workpiece centerline accurately.
- Apply steady, moderate pressure—do not force the tool.
- Clear chips regularly to avoid tool clogging and workpiece damage.
How to Select the Appropriate Lathe Parting Tool for Your Project
Selecting the right parting tool depends on several factors:
- Workpiece Material: Soft metals vs. hardened alloys require different tool types.
- Surface Finish Requirements: Sharp edges and high-quality materials like carbide or cermet improve finish.
- Production Volume: High-volume jobs demand long-lasting, durable tools.
- Machine Capabilities: The lathe’s speed, power, and stability should match the tool’s performance requirements.
- Cost vs. Longevity: Investing in durable materials may save time and cost in the long run.
Careful consideration of these factors ensures efficient, accurate, and safe machining operations.
Why Choose Precionn for Your Machining Solutions
In precision machining, the right tools make all the difference. Precionn offers a wide range of high-quality lathe parting tools designed for international customers. Each tool is manufactured to meet strict standards for accuracy, durability, and efficiency. From HSS to carbide and specialty materials, Precionn provides solutions that help machinists achieve clean cuts, reduced downtime, and reliable results.




